概述
InnoDB 是事务安全的 MySQL 存储引擎,通常来说,InnoDB 存储引擎是 OLTP 应用中核心表的首选存储引擎。被包括在 MySQL 数据库所有二进制发行版本中,从 MySQL 5.5 版本开始是默认的表存储引擎,其特点是行锁设计、支持 MVCC、支持外键、提供一致性非锁定读。
InnoDB 体系架构

后台线程
主要作用是负责刷新内存池中的数据,保证缓冲池中的内存缓存是最近的数据。此外将已修改的数据文件刷新到磁盘文件,同时保证在数据库发生异常的情况下 InnoDB 能恢复到正常运行状态。
Master Thread
最核心的后台线程,主要负责将缓冲池中的数据异步刷新到磁盘,保证数据的一致性,包括:脏页的刷新、合并插入缓冲(Insert Buffer)、Undo 页的回收等。
IO Thread
在 InnoDB 存储引擎中大量使用了 AIO(Async IO)来处理写 IO 请求,这样可以极大提高数据库的性能。而 IO Thread 的工作主要是负责这些 IO 请求的回调处理。共有四个线程:insert buffer thread、log thread、read thread、write thread。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27*************************** 1. row ***************************
Type: InnoDB
Name:
Status:
=====================================
2020-03-22 13:39:29 0x7f1f6e651700 INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
=====================================
Per second averages calculated from the last 17 seconds
...
--------
FILE I/O
--------
I/O thread 0 state: waiting for completed aio requests (insert buffer thread)
I/O thread 1 state: waiting for completed aio requests (log thread)
I/O thread 2 state: waiting for completed aio requests (read thread)
I/O thread 3 state: waiting for completed aio requests (read thread)
I/O thread 4 state: waiting for completed aio requests (read thread)
I/O thread 5 state: waiting for completed aio requests (read thread)
I/O thread 6 state: waiting for completed aio requests (write thread)
I/O thread 7 state: waiting for completed aio requests (write thread)
I/O thread 8 state: waiting for completed aio requests (write thread)
I/O thread 9 state: waiting for completed aio requests (write thread)
Pending normal aio reads: [0, 0, 0, 0] , aio writes: [0, 0, 0, 0] ,
ibuf aio reads:, log i/o's:, sync i/o's:
Pending flushes (fsync) log: 0; buffer pool: 0
4407465 OS file reads, 16740662 OS file writes, 580038 OS fsyncs
0.00 reads/s, 0 avg bytes/read, 0.00 writes/s, 0.00 fsyncs/sPurge Thread
事务被提交后,其所使用的 undolog 可能不再需要,因此需要 Purge Thread 来回收已经使用并分配的 undo 页。
1
2
3
4
5
6mysql> show variables like 'innodb_purge_threads';
+----------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------+-------+
| innodb_purge_threads | 4 |
+----------------------+-------+Page Cleaner Thread
其作用是将之前版本中脏页的刷新操作都放入到单独的线程中完成,进一步提高 InnoDB 存储引擎的性能。
内存
包括:缓冲池、Change 缓冲区、自适应哈希索引、Log 缓冲区。

缓冲池(Buffer Pool)
InnoDB 存储引擎是基于磁盘存储的,并将其中的记录按照页的方式进行管理。在数据库系统中,由于 CPU 速度和磁盘速度之间的鸿沟,基于磁盘的数据库系统通常使用缓冲池技术来提高数据库的整体性能。

缓冲池简单来说就是一块内存区域,通过内存的速度来弥补磁盘速度较慢对数据库性能的影响。
1)在数据库中进行读取的操作,首先将从磁盘读到的页存放在缓冲池中,下一次再读取相同的页时,首先判断该页是否在缓冲池中,若存在,称该页在缓冲池中被命中,直接读取该页,否则,读取磁盘上的页;
2)在数据中修改页的操作,首先修改在缓冲池中的页,然后再以一定的频率刷新到磁盘上,需要注意的是,页从缓冲池刷新回磁盘的操作并不是在每次页发生更新时触发,而是通过一种称为 CheckPoint 的机制刷新回磁盘。这也是为了提高数据库的整体性能。
对于 InnoDB 存储引擎而言,缓冲池的配置通过 innodb_buffer_pool_size 来设置,其大小直接影响着数据库的整体性能。
1 | mysql> show variables like 'innodb_buffer_pool_size'; |
需要注意的是,缓冲池不只是缓存索引页和数据页,还包括:undo 页、插入缓冲、自适应哈希索引、锁信息、数据字典信息等。
另外,InnoDB 支持通过参数 innodb_buffer_pool_instances 配置多个缓冲池实例,好处是减少数据库内部的资源竞争,增加数据库的并发处理能力。
1 | mysql> show variables like 'innodb_buffer_pool_instances'; |
1 | ---------------------- |
LRU
通常来说,数据库中的缓冲池是通过 LRU(Latest Recent Used,最近最少使用)算法进行管理。即最频繁使用的页在 LRU 列表的最前端,而最少使用的页在 LRU 列表的尾端。当缓冲池不能存放新读取到的页时,将首先释放 LRU 列表尾端的页。
InnoDB 存储引擎中,缓冲池中页的大小默认为 16KB,稍有不同的是 InnoDB 存储引擎对传统的 LRU 算法做了一些优化,在 LRU 列表中还加入了 Midpoint 位置,新读取到的页,虽然是最新访问的页,但并不是直接放入到 LRU 列表的首部,而是放入到 Midpoint 位置。默认配置下,该位置在 LRU 列表长度的 5/8 处。Midpoint 位置可由 innodb_old_blocks_pct 控制。可以理解为 New Sublist 中的页都是最为活跃的热点数据。参数 innodb_old_blocks_time 用于表示页读取到 Midpoint 位置后需要等待多久才会被加入到 LRU 列表的热端。
1 | mysql> show variables like 'innodb_old_blocks%'; |
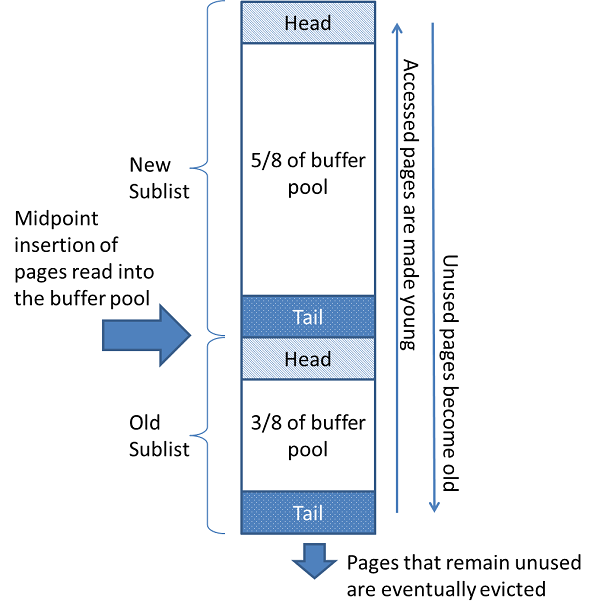
通常情况下,Buffer pool hit rate 不应该小于 95%,如果发生用户需要排查释放由于全表扫描引起 LRU 列表被污染的问题。
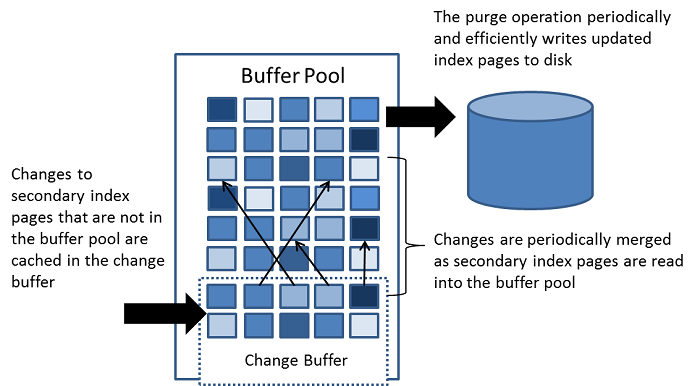
Change Buffer
在 LRU 列表中的页被修改后,称该页为脏页(dirty page),即缓冲池中的页和磁盘上的页的数据产生了不一致。这时数据库会通过 CheckPoint 机制将脏页刷新回磁盘,而 Flush 列表中的页即为脏页列表。需要注意的是,脏页既存在于 LRU 列表中,也存在于 Flush 列表中。LRU 列表用来管理缓冲池中页的可用性,Flush 列表用来管理将页刷新回磁盘,二者互不影响。
1 | ---------------------- |
1 | mysql> SELECT (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE |
Redo Log Buffer
InnoDB 存储引擎首先将重做日志信息放入到这个缓冲区,然后再按一定的频率将其刷新到重做日志文件。该值可由 innodb_log_buffer_size 控制。
1 | mysql> show variables like 'innodb_log_buffer_size'; |
重做日志在下面三种情况下会将重做日志缓冲内容刷新到外部磁盘的重做日志文件中:
- Master Thread 每一秒将重做日志缓冲刷新到重做日志文件;
- 每个事务提交时会将重做日志缓冲刷新到重做日志文件;
- 当重做日志缓冲池剩余空间小于 1/2 时,重做日志缓冲刷新到重做日志文件;
InnoDB 关键特性
- 插入缓冲(Insert Buffer)
- 两次写(Double Write)
- 自适应哈希索引(Adaptive Hash Index)
- 异步 IO(Async IO)
- 刷新临近页(Flush Neighbor Page)