ORM
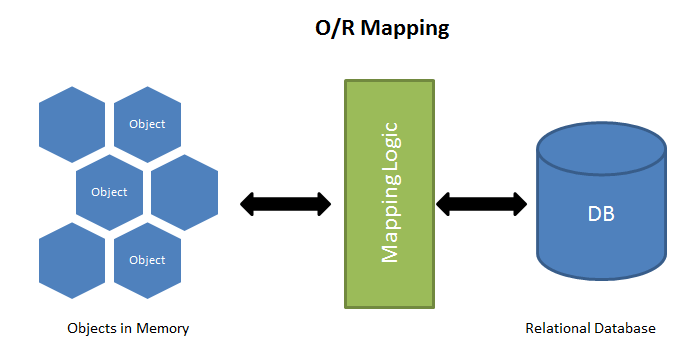
简单说,ORM 就是通过实例对象的语法,完成关系型数据库的操作的技术,对象-关系映射(Object/Relational Mapping) 的缩写,ORM 的主要功能是把数据库映射成对象。
数据库表(table)–> 类(class)
记录(record,行数据)–> 对象(object)
字段(field)–> 对象的属性(attribute)
示例
1 | # 数据库写法 |
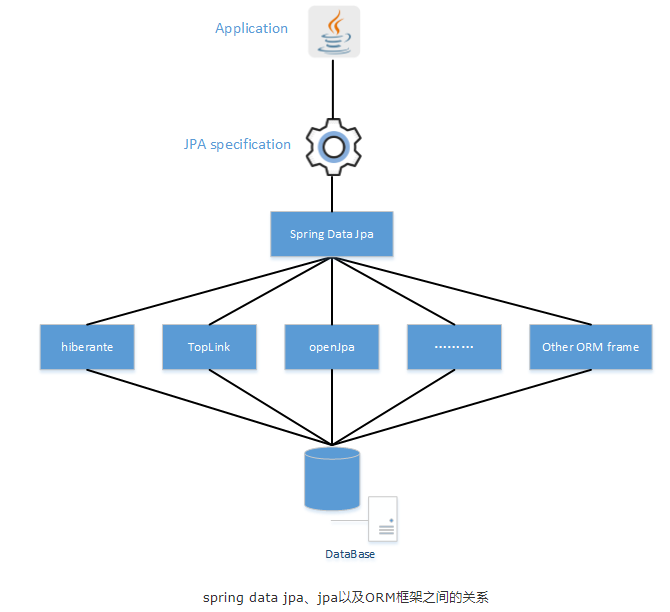
现在 Dao 持久层的解决方案中,大部分是采用 Spring Data JPA 或 MyBatis 解决方案,并且传统企业多用前者,互联网企业多用后者。Spring Data JPA 是 Spring Data 在 JPA 和 ORM 框架之间抽象封装层,它不直接代替 ORM 框架,默认低层使用的 ORM 框架是 Hibernate。
JPA
Java Persistence API,可以通过注解或者 XML 描述对象-关系表之间的映射关系,并将实体对象持久化到数据库中,JPA 是一套 ORM 规范。
Spring Data JPA:是 Spring 提供的一套简化 JPA 开发的框架,按照约定好的方法命名规则写 dao 层接口,就可以在不写接口实现的情况下,实现对数据库的访问和操作,可以理解为 JPA 规范的再次封装抽象,底层还是使用了 Hibernate 的 JPA 技术实现。
接口约定命名规则
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL snippet |
|---|---|---|
And |
findByLastnameAndFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
Or |
findByLastnameOrFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
Is, Equals |
findByFirstname,findByFirstnameEquals |
… where x.firstname = ?1 |
Between |
findByStartDateBetween |
… where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
LessThan |
findByAgeLessThan |
… where x.age < ?1 |
LessThanEqual |
findByAgeLessThanEqual |
… where x.age <= ?1 |
GreaterThan |
findByAgeGreaterThan |
… where x.age > ?1 |
GreaterThanEqual |
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual |
… where x.age >= ?1 |
After |
findByStartDateAfter |
… where x.startDate > ?1 |
Before |
findByStartDateBefore |
… where x.startDate < ?1 |
IsNull, Null |
findByAge(Is)Null |
… where x.age is null |
IsNotNull, NotNull |
findByAge(Is)NotNull |
… where x.age not null |
Like |
findByFirstnameLike |
… where x.firstname like ?1 |
NotLike |
findByFirstnameNotLike |
… where x.firstname not like ?1 |
StartingWith |
findByFirstnameStartingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?% |
EndingWith |
findByFirstnameEndingWith |
… where x.firstname like %? |
Containing |
findByFirstnameContaining |
… where x.firstname like %?% |
OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc |
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
Not |
findByLastnameNot |
… where x.lastname <> ?1 |
In |
findByAgeIn(Collection ages) |
… where x.age in ?1 |
NotIn |
findByAgeNotIn(Collection ages) |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
True |
findByActiveTrue() |
… where x.active = true |
False |
findByActiveFalse() |
… where x.active = false |
IgnoreCase |
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase |
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |
maven 坐标
1 | <dependency> |
yml 配置
1 | #配置数据源 |
JPA vs MyBatis
Mybatis
优点:
- SQL 语句可以自由控制,更灵活,性能更高
- SQL 与代码分离,易于阅读和维护
- 提供 XML 标签,支持动态 SQL 语句
缺点:
- 简单 CRUD 操作还得写 SQL 语句
- XML 中有大量的 SQL 需要维护
- MyBatis 自身功能有限,但支持 Plugin
JPA
优点:
- 移植性比较好
- 提供了很多 CRUD 方法,开发效率高
- 对象化程度高
缺点:
- 框架比较重,学习成本较高
- 性能不好控制